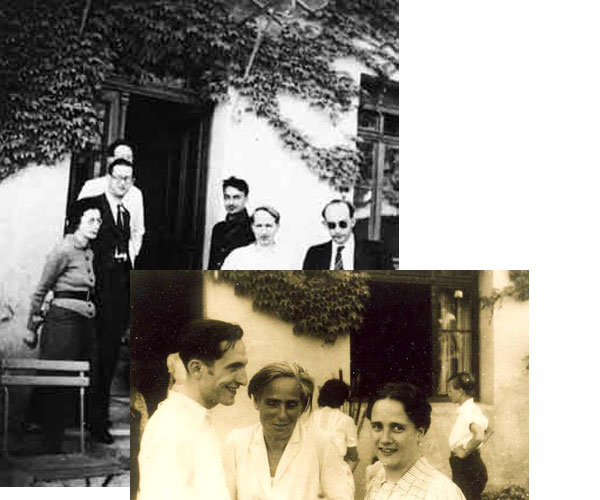
Early on in this series we deciphered part of the Bourbaki wedding invitation

The wedding was planned on “le 3 Cartembre, an VI” or, for non-Bourbakistas, June 3rd 1939. But, why did they choose that particular day?
Because the wedding-invitation-joke was concocted sometime between mid april and mid may 1939, the most probable explanation clearly is that they took a calendar and scheduled their fake wedding on a saturday not too far in the future.
Or, could it be that the invitation indeed contained a coded message pointing to an important event (at least as far as Bourbaki or the Weils were concerned) taking place in Paris on June 3rd 1939?
Unlikely? Well, what about this story:
 André Malraux was a French writer and later statesman. He was noted especially for his novel La Condition Humaine (1933).
André Malraux was a French writer and later statesman. He was noted especially for his novel La Condition Humaine (1933).
During the 1930s, Malraux was active in the anti-fascist Popular Front in France. At the beginning of the Spanish Civil War he joined the Republican forces in Spain, serving in and helping to organize the small Spanish Republican Air Force. The Republic government circulated photos of Malraux’s standing next to some Potez 540 bombers suggesting that France was on their side, at a time when France and the United Kingdom had declared official neutrality.
In 1938 he published L’Espoir, a novel influenced by his Spanish war experiences. In the same year, Malraux and Boris Peskine produced a movie based on the book, filmed in Spain (in Tarragon, Collbató and Montserrat) : sierra de Teruel (later called, L’Espoir)
 This wikipedia-page claims that the movie was released June 13th, 1945. But this isn’t quite correct.
This wikipedia-page claims that the movie was released June 13th, 1945. But this isn’t quite correct.
The first (private) viewing of the film took place … on saturday june 3rd, 1939.
In august 1939 there was another private viewing for the Spanish Government-in-Exile, and Malraux wanted the public release to take place in september. However, after the invasion by Hitler of Poland and considerable pressure of the French amassador to Madrid, Philippe Petain, the distribution of the movie was forbidden by the government of Edouard Daladier IV.
For this reason the public release had to be postponed until after the war.
But let us return to the first viewing on Bourbaki’s wedding day. We know that a lot of authors were present. There’s evidence that Simone de Beauvoir attended and quite likely so did Simone Weil, Andre’s sister.
In 1936, despite her professed pacifism, Simone Weil fought in the Spanish Civil War on the Republican side. She identified herself as an anarchist and joined the Sébastien Faure Century, the French-speaking section of the anarchist militia.
According to her biography (p. 473) she was still in contact with Malraux and, at the time, tried in vain to convince him of the fact that the Stalin-regime was as oppressive as the fascist-regimes. So, it is quite likely she was invited to the viewing, or at least knew about it.
From Andre Weil’s auto-biography we know that letters (and even telegrams) were exchanged between him and his sister, when he was in England in the spring of 1939. So, it is quite likely that she told him about the Malraux-Sierra de Tenuel happening (see also the Escorial post).
According to the invitation the Bourbaki-wedding took place “en la Cohomologie Principale”. The private viewing of Malraux’ film took place in “Cinéma Le Paris” on the Champs Elysées.
Could it be that “Cohomologie Principale”=”Cinema Le Paris”?
Leave a Comment First, the few facts we know about this Bourbaki congress, mostly from
First, the few facts we know about this Bourbaki congress, mostly from